Distal radioulnar joint surgery
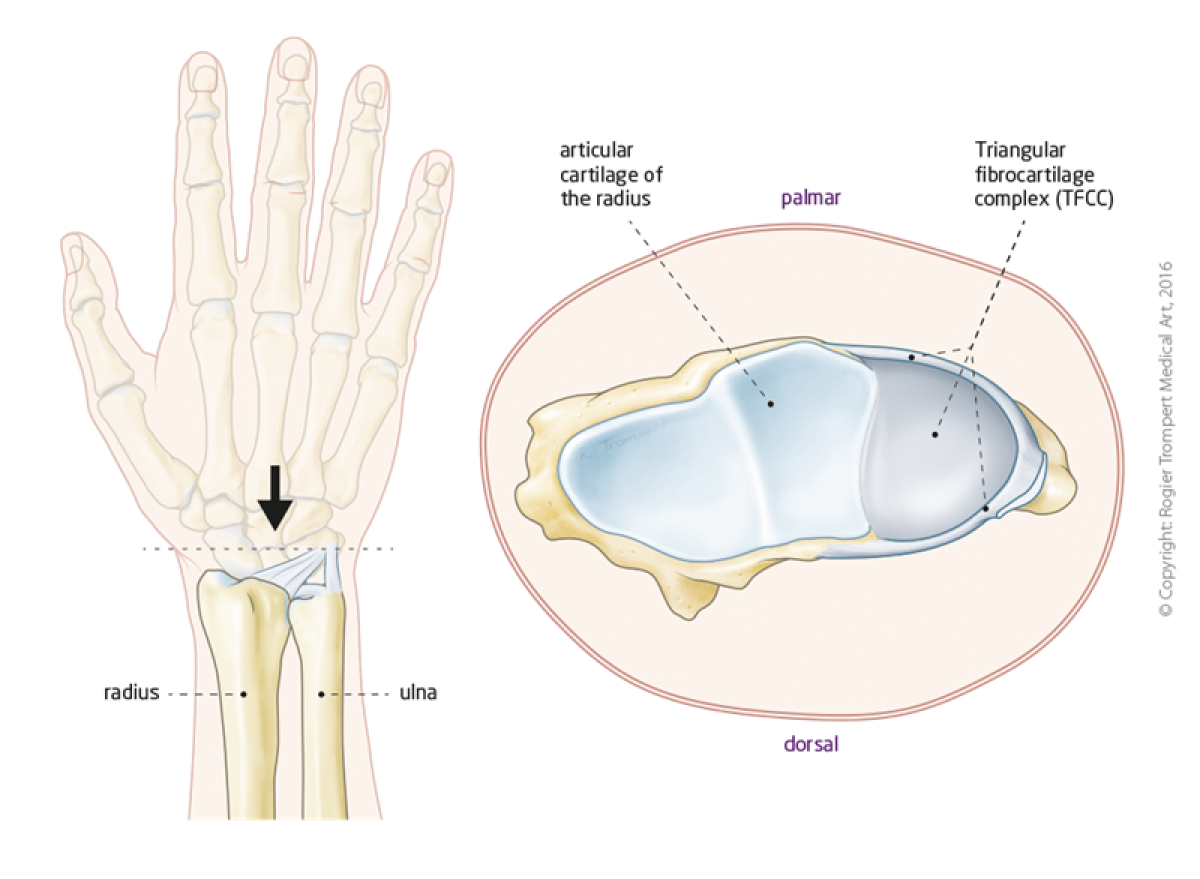
The two forearm bones are the ulna and the radius. When one rotates the forearm the radius rotates over the ulna at the wrist at the distal radioulnar (DRU) joint. Stability of this joint is mainly provided by surrounding soft tissues: the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC).
Injury, overuse or degenerative changes can cause functional problems of the DRU joint. Symptoms typically include pain at the little finger side of the wrist, reduced forearm rotation, wrist weakness or clicking or clunking of the wrist during certain movements.
Surgery to stabilise, reconstruct, replace or remove the joint can provide relief of symptoms and improved function.
In most cases, recovery includes splinting and intensive hand therapy for weeks or months.